significance DriverLayer Search Engine

3) STATISTICAL ASSUMPTIONS. Statistical tests make some common assumptions about the data being tested (If these assumptions are violated then the test may not be valid: e.g. the resulting p-value may not be correct). Independence of observations: the observations/variables you include in your test should not be related(e.g. several tests from a same test subject are not independent, while.
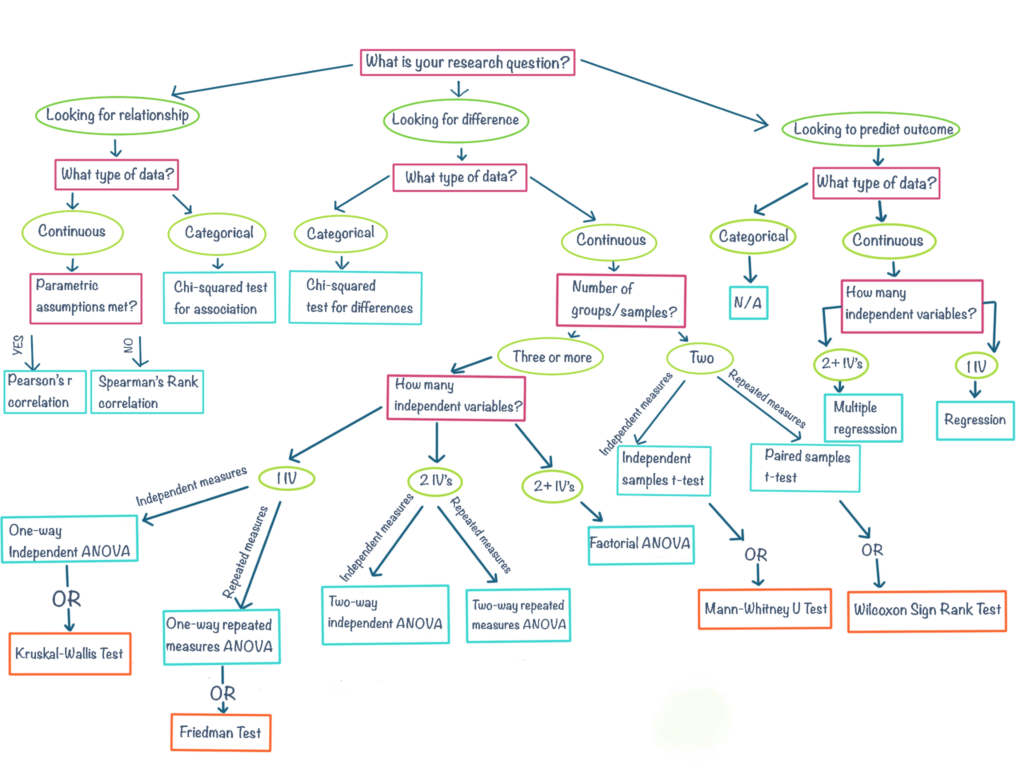
How to select statistical procedures
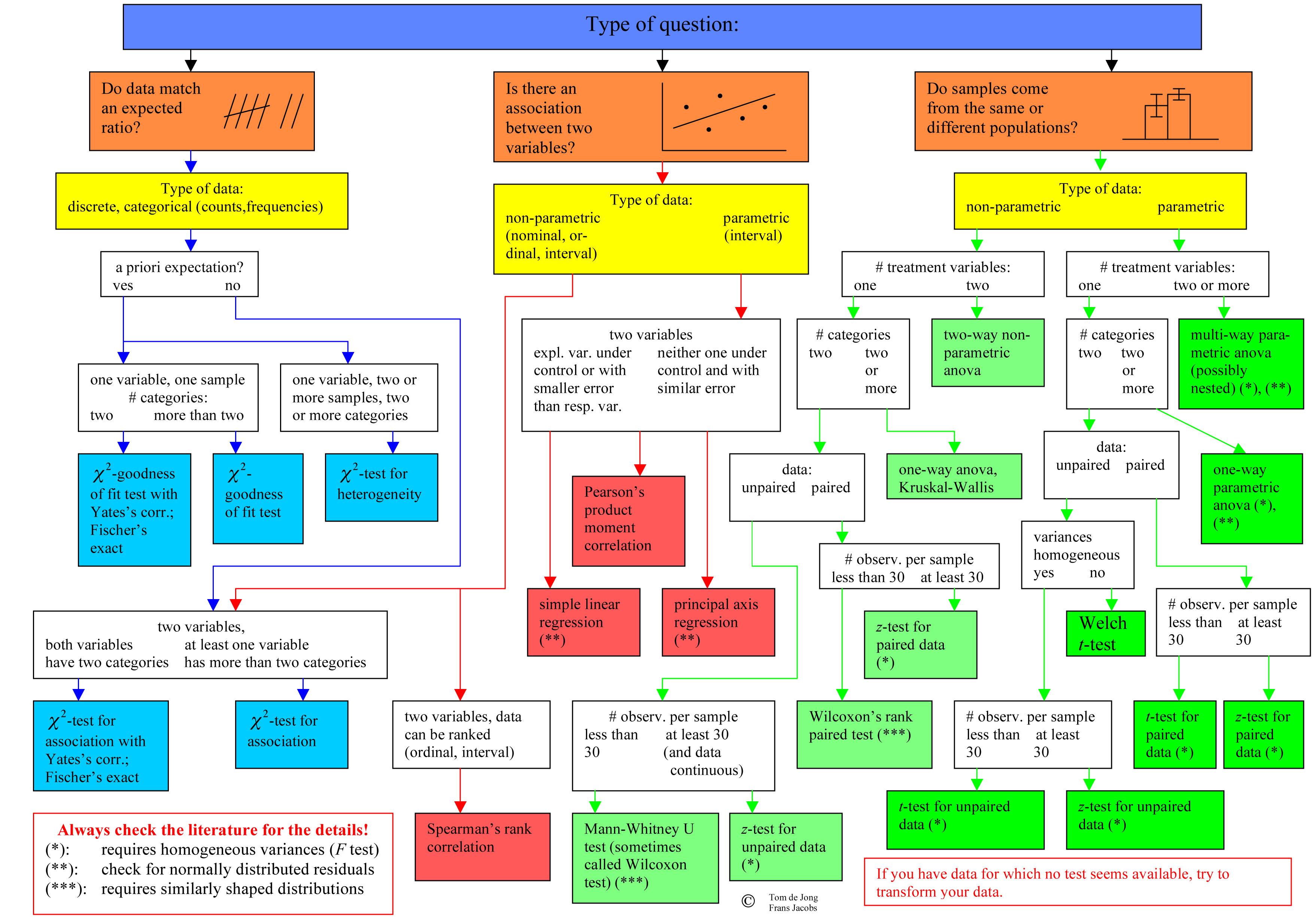
Chi-square test of goodness-of-fit. 1 1. -. -. test fit of observed frequencies to expected frequencies. use for large sample sizes (greater than 1000 1000) count the number of red, pink and white flowers in a genetic cross, test fit to expected 1: 2: 1 1: 2: 1 ratio, total sample > 1000 > 1000.
How to choose the right statistical test Statistical Aid
It is important to choose a test that aligns with the nature of your data, the type of comparison you want to make, and any specific assumptions or conditions that need to be met. Here are some essential things to consider while choosing the right statistical test: 1. Research question. 2.
Statistics Final Exam Cheat Sheet Cheat Dumper

6O;k ik;kPikPD;Y kHik iO]lYF F]¨ ]r Z;[t. q;hP;CYHi¨ q;hP;CYH q;hP;CYHi. Ü q;hP;CYHi,l;YPk;kPqH,l;[kPk;kPqH Nh]lei. Ü Nh]lei
Flow Chart for Selecting Commonly Used Statistical Tests Sociology and Social Research

Blue Segment: You are conducting a univariate analysis, so you should be checking the larger of the 2 Hypothesis Wheels and you should locate the entry of UV. Orange Segment: This is where The Hypothesis Wheel reveals the correct statistical test to use for your study: Step 4 - Choosing the Correct Statistical Test:
Flowchart what statistical test do I do not significant significant no What statistical test
The most important consideration in choosing a statistical test is determining what hypothesis you want to test. Or, more generally, what question are you are trying to answer. Often people have a notion about the purpose of the research they are conducting, but haven't formulated a specific hypothesis. It is possible to begin with.
Statistics Science without sense…double nonsense
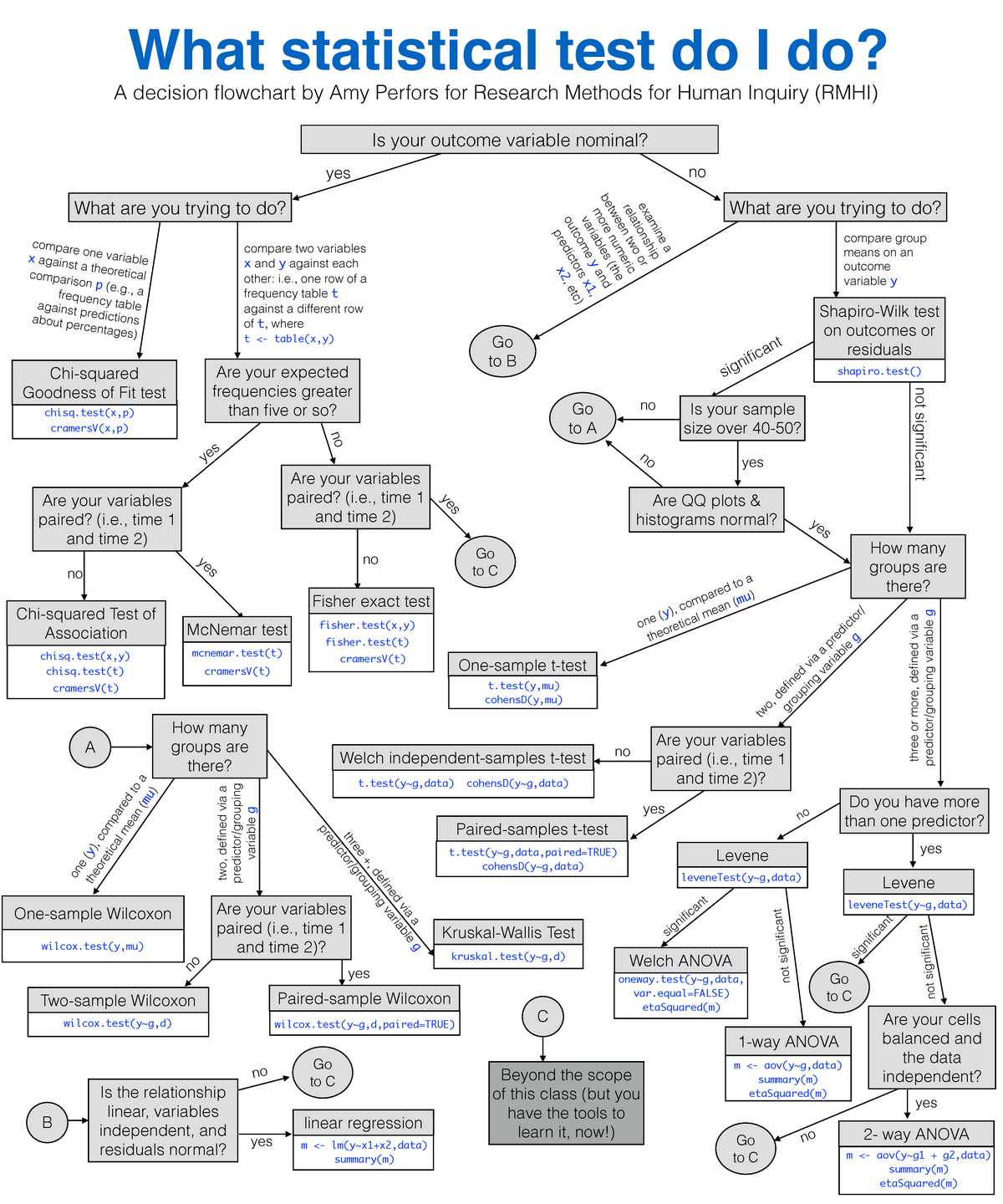
A flowchart. A flowchart to decide what hypothesis test to use. Many years ago I taught a stats class for which one of the topics was hypothesis testing. Many of the students had a hard time remembering what situation each test was designed for, so I made a flowchart to help piece together the wild world of hypothesis tests.
Statistics SPS Quantitative Reasoning Resources

If this is not the case, the nonparametric version (i.e., the Wilcoxon test) should be preferred. The same goes for ANOVA and many other statistical tests. The flowchart could be extended to include more advanced linear or non-linear models, but this is beyond its scope and goal. Remember that I created it to help non-experts to see more.
Types of Statistical Analysis ArianarosBradshaw

Statistical Test Flow Chart Geo 441: Quantitative Methods Part B - Group Comparison II Normal Non-Normal 1 Sample z Test 2 Sample (Independent) t Test for equal variances Paired Sample t Test Compare two groups Compare more than two groups 1- Way AOV F Test One group Non-paired data Paired data
Which hypothesis test should I use? A flowchart

When comparing more than two sets of numerical data, a multiple group comparison test such as one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) or Kruskal-Wallis test should be used first. If they return a statistically significant p value (usually meaning p < 0.05) then only they should be followed by a post hoc test to determine between exactly which two.
Four common statistical test ideas to share with your academic colleagues
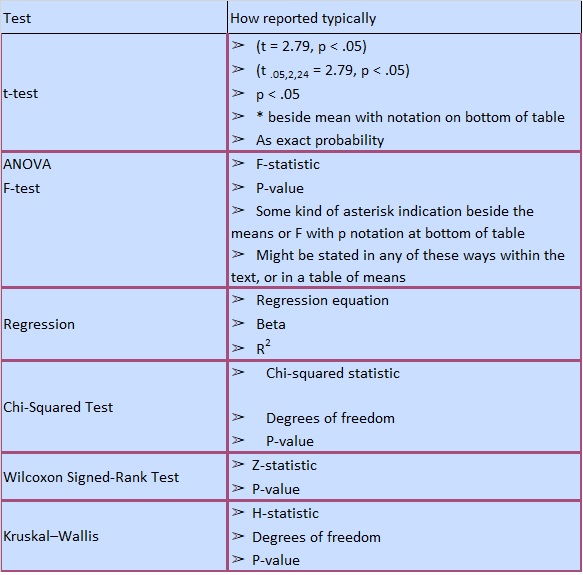
Exact test for goodness-of-fit. 1. -. -. test fit of observed frequencies to expected frequencies. use for small sample sizes (less than 1000) count the number of red, pink and white flowers in a genetic cross, test fit to expected 1:2:1 ratio, total sample <1000. Chi-square test of goodness-of-fit. 1.
Student T Test Table Two Tailed
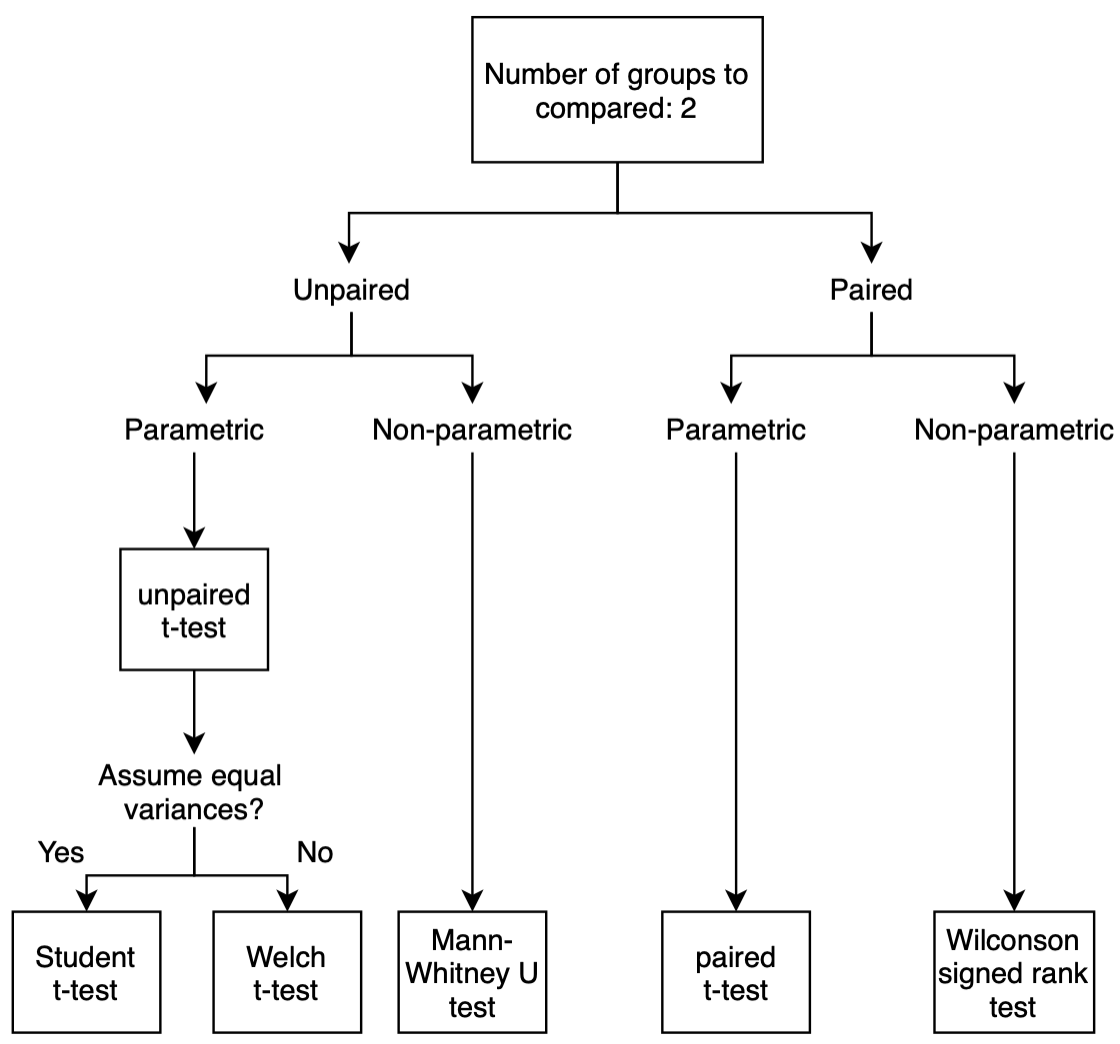
We help you decide which statistical test is right for you based on your question and your data. Choose Your StatsTest. If you aren't sure where to start, feel free to explore our StatsTest flow chart—a graphic depiction of all of the methods we cover here at StatsTest.com. Answer the questions to see which method to pick based on your.
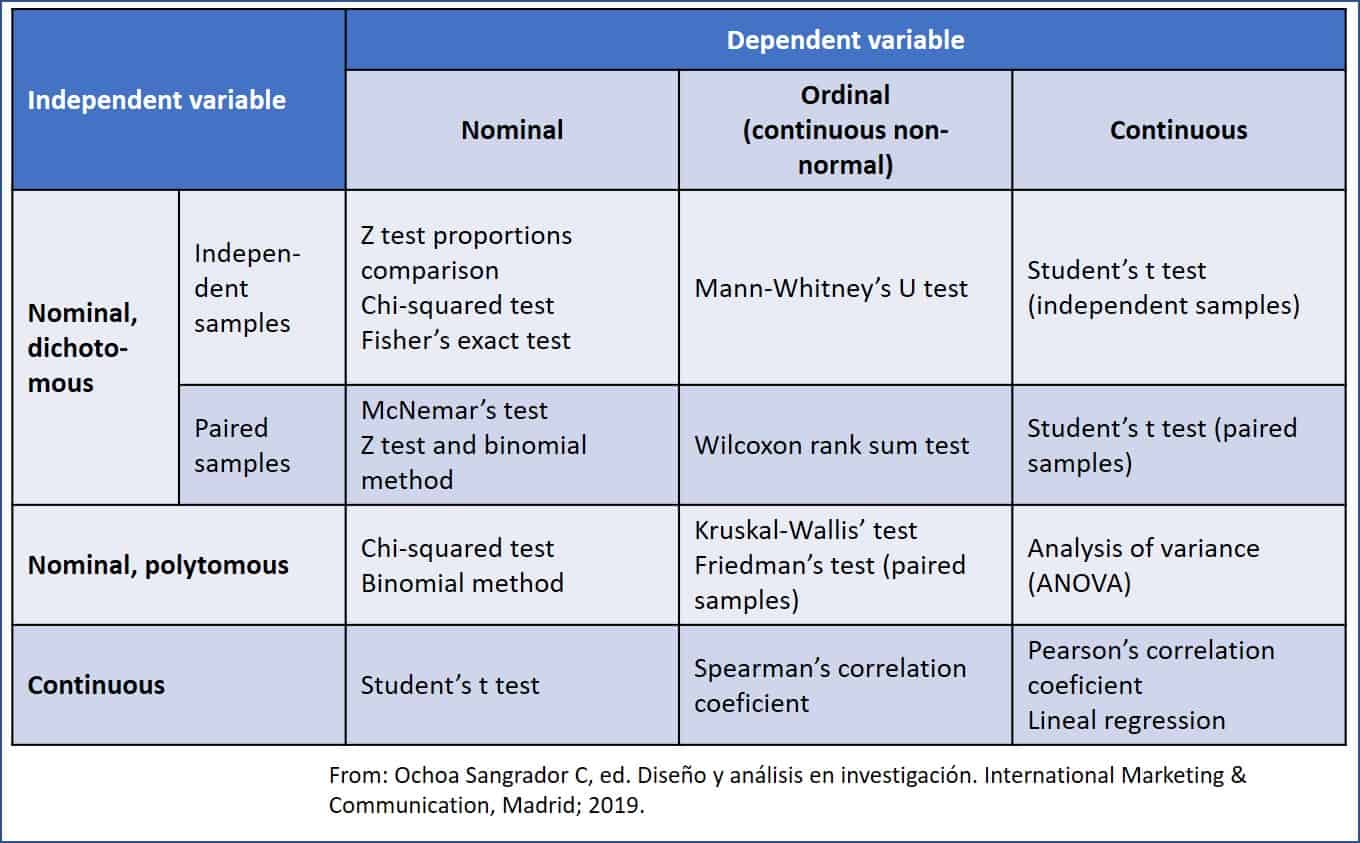
Flowchart for selecting a statistical test for numerical Download Scientific Diagram

Assumptions: testing the assumptions required for a statistical analysis. Equality of variance: Data are normally distributed - Levene's test, Bartlett test (also Mauchly test for sphericity in repeated measures analysis). Data are non-parametric - Ansari-Bradley, Mood test, Fligner-Killeen test.
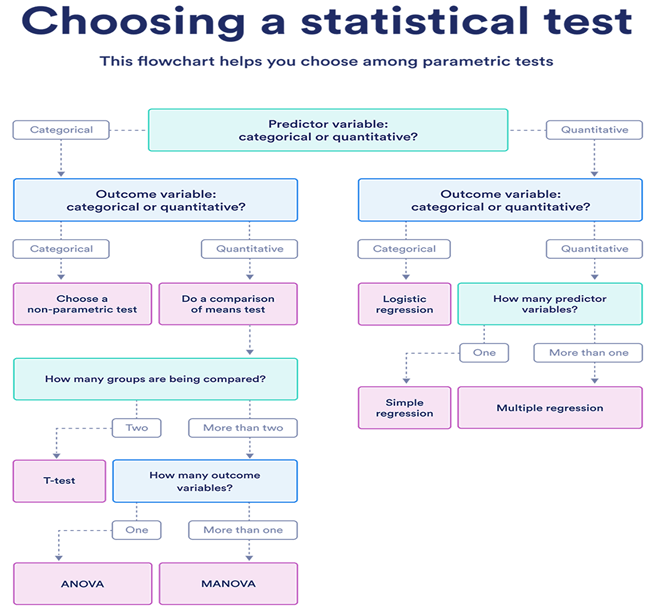
Choosing the Right Statistical Test
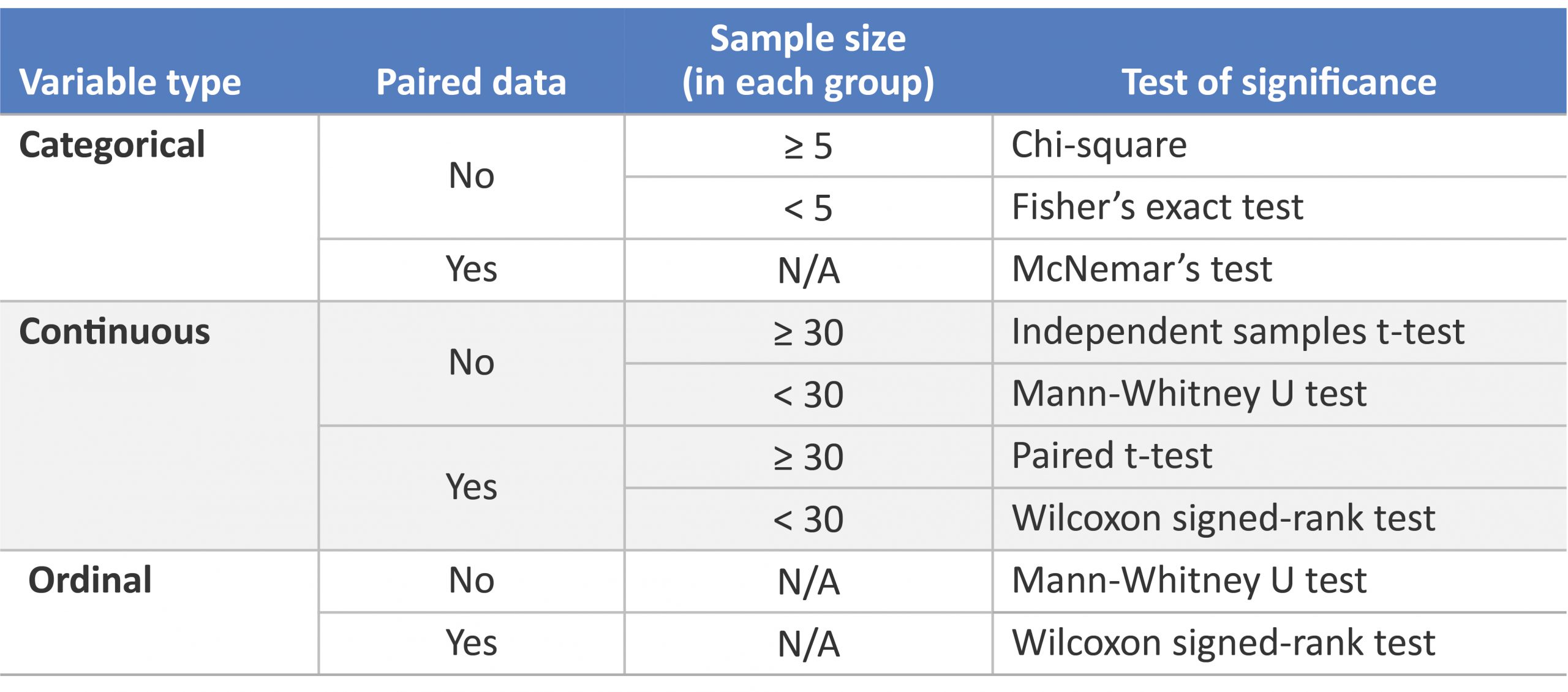
Categorical variables represent groupings of things (e.g. the different tree species in a forest). Types of categorical variables include: Ordinal: represent data with an order (e.g. rankings). Nominal: represent group names (e.g. brands or species names). Binary: represent data with a yes/no or 1/0 outcome (e.g. win or lose).
Choosing a Statistical Test YouTube
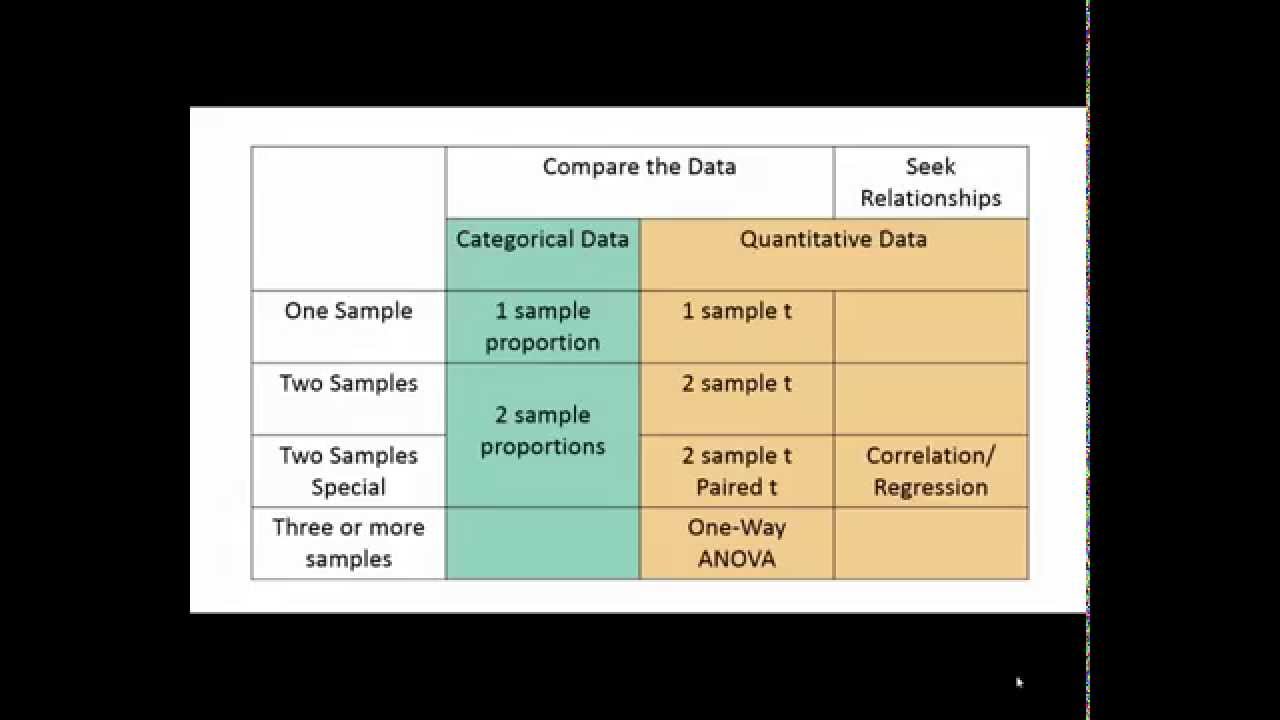
Real-World Examples of Statistical Test Selection. Example 1: A/B Testing for Website Optimization. Example 2: Customer Satisfaction across Age Groups. Example 3: Examining the Relationship between Variables. Common Mistakes to Avoid When Choosing a Statistical Test. Mistake 1: Ignoring the data type.
Stats Bites Choosing your Analysis Digital Education Resources
A useful guide is to use a Bonferroni correction, which states simply that if one is testing n independent hypotheses, one should use a significance level of 0.05/n. Thus if there were two independent hypotheses a result would be declared significant only if P < 0.025.
.